Silicon dioxide is a chemical compound with a molecular formula SiO2. It is most commonly found in nature as quartz. It exists as either white or colourless crystals. Silicon dioxide is also known as silica, silicic acid and silicic acid anhydride. Silica is non-combustible and is the most abundant mineral found on earth. In this article, let us learn more about the silicon dioxide formula, its chemical structure, general properties and uses.
Properties of Silicon Dioxide
| Silicon dioxide Properties | |
| Name | Silicon dioxide |
| Also Known as | Silica, Silic acid and Silic acid anhydride |
| Appearance | Transparent solid (amorphous)
White/Whitish yellow (sand/powder) |
| Molecular Formula | SiO2 |
| Melting Point | 1,710 °C |
| Boiling Point | 2,230 °C |
| Density | 2.65 g/cm³ (α-quartz)
2.196 g/cm³ (amorphous) |
| Molar Mass | 60.08 g/mol |
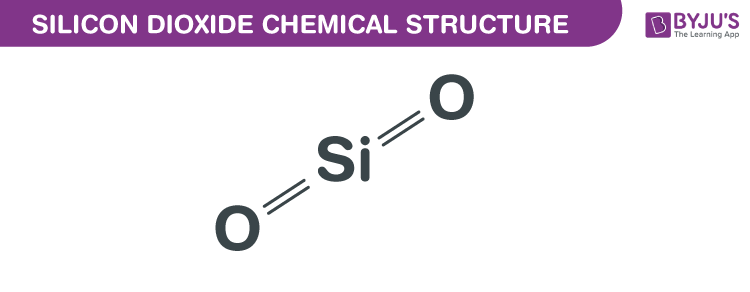
Silicon Dioxide Chemical Structure
Silicon Dioxide Uses
- Used in the production of adhesives, ceramic, porcelain, corrosion inhibitors and paint additives
- Used in the production of agricultural chemicals
- It is the main component in optical fibres in telecommunication.
Recommended Videos

To learn more about such chemistry topics register to BYJU’S now!
Comments